Introduction
Managing exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) requires careful attention to how pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy interacts with different foods. One frequently asked question among Creon users involves whether bananas specifically require enzyme supplementation or if this combination offers particular benefits. The relationship between pancreatic enzymes and fruit consumption can significantly impact nutrient absorption and digestive comfort for individuals with compromised pancreatic function.
Understanding the compatibility between Creon and various foods empowers patients to make informed dietary choices while maximizing therapeutic outcomes. This comprehensive guide examines the scientific rationale behind taking Creon with bananas, explores optimal timing strategies, and provides evidence-based recommendations for enhancing enzyme effectiveness through strategic food pairing.
Understanding Creon and Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement
How Creon Works
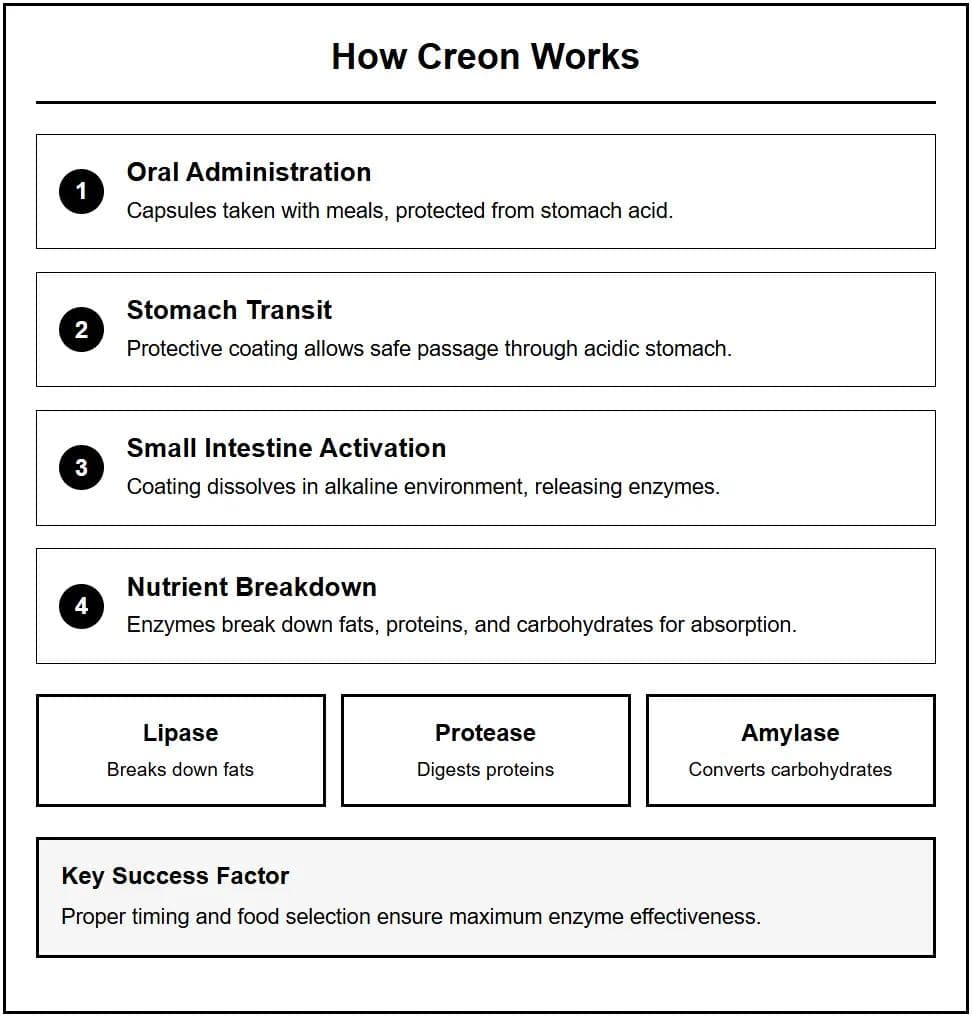
Creon represents a sophisticated pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy containing pancrelipase, a comprehensive mixture of digestive enzymes derived from porcine pancreatic tissue. The medication delivers three essential enzyme categories: lipases for fat digestion, proteases for protein breakdown, and amylases for carbohydrate processing. This pharmaceutical formulation utilizes enteric-coated microspheres that protect enzymes from gastric acid degradation while ensuring optimal release within the small intestine's alkaline environment.
Conditions Requiring Creon
The therapeutic indication for Creon encompasses several serious medical conditions that compromise pancreatic enzyme production. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) serves as the primary diagnosis, manifesting in patients with cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis, or following pancreatectomy procedures. Additional conditions include type 2 diabetes with pancreatic complications, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome, and certain autoimmune disorders affecting pancreatic function.
Each condition presents unique challenges regarding enzyme replacement needs and dietary management strategies. Cystic fibrosis patients typically require lifelong enzyme therapy due to genetic mutations affecting chloride channels, while chronic pancreatitis patients may experience variable enzyme needs depending on disease progression and inflammatory episodes.
Why Proper Food Pairing Matters
Strategic food selection directly influences enzyme activation and therapeutic outcomes for Creon users. The medication's enteric coating responds to pH changes, requiring acidic food environments for optimal dissolution timing. Furthermore, macronutrient composition affects enzyme utilization efficiency, with balanced meals providing superior nutrient absorption compared to isolated food consumption.
⚠️ Critical Timing Factor: Enzyme effectiveness diminishes rapidly without simultaneous food presence, making proper meal coordination essential for therapeutic success.
Can You Take Creon with a Banana?
Direct Answer: Banana Compatibility
Yes, you can safely take Creon with a banana, and this combination offers several digestive advantages for individuals managing EPI. Bananas possess favorable characteristics that complement pancreatic enzyme therapy, including moderate fiber content, natural enzymes, and gentle digestive properties that rarely trigger gastrointestinal distress.
The fruit's naturally acidic pH (approximately 4.5-5.2) aligns well with Creon's activation requirements, though bananas fall near the threshold between acidic and neutral foods. This positioning makes them suitable for enzyme therapy while avoiding the complications associated with highly alkaline foods that can interfere with proper enzyme release.
Nutritional Profile and Digestive Considerations
Bananas provide a complex nutritional matrix that benefits EPI patients beyond simple caloric content. Each medium banana contains approximately:
| Nutrient Component | Amount per Medium Banana | EPI Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Fiber | 3.1 grams | Supports digestive health but may require enzyme assistance |
| Potassium | 422 milligrams | Essential electrolyte enhanced by proper enzyme function |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.4 milligrams | Supports protein metabolism aided by protease enzymes |
| Natural Sugars | 14 grams | Easily digestible carbohydrates requiring amylase activity |
| Resistant Starch | Variable | Prebiotic benefits with proper enzyme support |
The fruit's soluble fiber content, primarily pectin, can be challenging for compromised digestive systems without adequate enzyme support. However, when combined with appropriate Creon dosing, these fibers contribute to improved gut health and nutrient absorption efficiency.
Benefits of the Combination
Taking Creon with bananas enhances several physiological processes that support overall digestive wellness. The enzyme supplementation ensures complete breakdown of the fruit's complex carbohydrates and fiber components, preventing malabsorption symptoms like bloating, gas, or incomplete nutrient utilization.
Research Insight: Studies indicate that proper enzyme replacement therapy can improve potassium absorption from fruits by up to 35% compared to unsupplemented consumption in EPI patients.
Additionally, bananas' natural enzyme content, including amylase and glucose oxidase, works synergistically with Creon's pharmaceutical enzymes to optimize carbohydrate digestion. This complementary action reduces the digestive burden on compromised pancreatic function while maintaining nutritional benefits.
🍌 Pro Tip: Slightly green bananas contain higher resistant starch levels, which may require additional enzyme support but provide superior prebiotic benefits for gut microbiome health.
How Bananas Interact with Creon Effectiveness
Fiber Content Impact on Enzyme Function
The soluble and insoluble fiber components within bananas create both opportunities and challenges for pancreatic enzyme therapy. Soluble fiber, primarily pectin, forms gel-like substances in the digestive tract that can slow enzyme-food mixing but also provides sustained nutrient release. Insoluble fiber adds bulk and promotes intestinal motility, potentially affecting enzyme contact time with food particles.
Excessive fiber intake (above 25 grams daily) can reduce Creon effectiveness by binding enzymes and preventing optimal food interaction. However, the moderate fiber content in a single banana (3.1 grams) rarely approaches problematic levels, especially when distributed throughout daily meal planning.
- Pectin benefits: Supports healthy cholesterol levels and blood sugar control
- Cellulose effects: Promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation
- Enzyme interaction: Requires adequate lipase and protease for complete fiber breakdown
Potassium Absorption Enhancement
Bananas rank among the highest potassium-containing fruits, providing essential electrolyte support for cardiovascular and muscle function. EPI patients often experience electrolyte imbalances due to malabsorption issues, making effective potassium utilization crucial for overall health maintenance.
Creon's enzyme action facilitates cellular membrane transport mechanisms that enhance potassium bioavailability. Protease enzymes break down protein carriers that transport potassium across intestinal walls, while lipase activity supports fat-soluble vitamin absorption that regulates electrolyte balance.
💡 Absorption Strategy: Combining bananas with small amounts of healthy fats (like nut butter) can further enhance potassium absorption while providing optimal conditions for Creon activation.
Low-Fat Nature Benefits
Bananas contain minimal fat content (less than 0.5 grams per medium fruit), making them ideal snacks for EPI patients who may struggle with fat digestion. This characteristic reduces the lipase enzyme demand while still providing substantial nutritional value through carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
The low-fat profile also minimizes risks of steatorrhea (fatty stools) that can occur when enzyme dosing doesn't match fat intake. For patients adjusting to Creon therapy or managing dose optimization, bananas offer nutritional security without overwhelming compromised digestive capacity.
| Fat Content Comparison | Grams per Serving | Enzyme Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Banana | 0.4g | Minimal lipase required |
| Medium Apple | 0.3g | Minimal lipase required |
| Medium Avocado | 21g | High lipase demand |
| Handful of Nuts | 14g | Moderate lipase demand |
Optimal Ways to Take Creon with Bananas
Timing Recommendations
Take Creon immediately before consuming your banana to ensure optimal enzyme availability when food reaches the small intestine. The enteric-coated spheres require approximately 30-60 minutes to transit the stomach and begin releasing enzymes, making pre-meal administration crucial for therapeutic effectiveness.
For banana consumption as a snack, follow these timing guidelines:
- 5 minutes before eating: Optimal timing for most patients
- With the first bite: Acceptable alternative for those who forget pre-dosing
- Never after finishing: Reduces enzyme effectiveness significantly
🕐 Timing Tip: Set reminders on your phone to take Creon before snacks, as irregular timing can lead to digestive discomfort and reduced nutrient absorption.
Proper Swallowing Technique
Always swallow Creon capsules whole with adequate liquid (at least 8 ounces of water) to ensure proper stomach transit and prevent capsule lodging in the esophagus. Never crush, chew, or break open capsules unless specifically instructed by your healthcare provider for pediatric administration.
If swallowing difficulties persist, the capsule contents can be sprinkled on acidic foods like applesauce, but this should be consumed immediately without chewing the enzyme spheres. When taking Creon before eating a banana, choose room temperature or cool beverages to avoid heat damage to enzyme activity.
⚠️ Safety Warning: Hot beverages can denature pancreatic enzymes, significantly reducing their digestive effectiveness and potentially causing mouth irritation if capsules are opened.
Portion Considerations and Dosage Adjustments
Standard snack dosing typically involves half the meal dose, but banana consumption may require individualized adjustments based on ripeness and accompanying foods. Ripe bananas contain higher sugar concentrations requiring increased amylase activity, while green bananas have more resistant starch demanding additional enzyme support.
Consider these portion-based dosing strategies:
- Small banana (6 inches): Standard snack dose
- Large banana (8+ inches): Consider meal-level dosing
- Multiple bananas: Definitely requires meal-dose enzyme support
- Banana smoothies: May need increased dosing due to volume and added ingredients
📊 Dosage Guideline: Consult your healthcare provider if regularly consuming large portions of fruit or adding high-fat ingredients like nut butters to banana-based snacks.
Foods That Work Well vs. Poorly with Creon
Best Food Combinations
Strategic food pairing maximizes Creon's therapeutic potential while minimizing digestive complications. Acidic foods create optimal conditions for enteric coating dissolution, while balanced macronutrient profiles ensure comprehensive enzyme utilization across all digestive pathways.
Excellent Creon-compatible foods include:
- Citrus fruits: Natural acidity enhances enzyme activation
- Yogurt with probiotics: Supports gut health and provides protein for protease activity
- Lean proteins: Optimize protease enzyme function
- Complex carbohydrates: Provide sustained amylase utilization
- Healthy fats in moderation: Allow lipase enzymes to function effectively
Nutritionist Recommendation: "Combining multiple food groups in each meal ensures comprehensive enzyme activation and prevents nutrient deficiencies common in EPI patients."
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can significantly impair Creon effectiveness or trigger digestive complications in EPI patients. High-alkaline foods neutralize stomach acid prematurely, causing enzyme release in inappropriate digestive locations where they cannot function optimally.
| Food Category | Specific Examples | Why to Avoid | Alternative Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-acidic liquids | Milk, alkaline water | Interferes with enzyme release | Water, acidic juices |
| Extremely hot foods | Hot soup, coffee | Denatures enzyme proteins | Room temperature versions |
| Excessive fiber | Large salads, bran cereals | Binds enzymes, reduces contact | Moderate portions with enzymes |
| High-fat meals | Fried foods, fatty meats | Overwhelms lipase capacity | Lean proteins with healthy fats |
🚫 Absolute Avoidances: Never take Creon with antacids, alkaline beverages, or extremely hot foods that can destroy enzyme activity before reaching the intended digestive location.
Creating Effective Meal Plans
Successful EPI management requires systematic meal planning that optimizes enzyme utilization while meeting nutritional requirements. Consistent meal timing helps establish digestive rhythms, while balanced macronutrient distribution ensures comprehensive enzyme activation throughout the day.
Effective meal planning strategies include:
- Regular meal intervals: Every 3-4 hours to maintain digestive stability
- Snack incorporation: Planned enzyme-supported snacks prevent nutrient gaps
- Hydration emphasis: Adequate fluid intake supports enzyme function and nutrient transport
- Variety prioritization: Diverse foods prevent nutrient deficiencies and maintain interest
📝 Planning Tool: Keep a food and symptom diary to identify optimal food combinations and timing patterns that work best for your individual digestive response.
Dosage Considerations When Eating Bananas
Standard Dosing Guidelines
Creon dosing for banana consumption typically follows snack-level protocols, generally requiring half the prescribed meal dose unless consumed with substantial additional foods. The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation recommends basing enzyme dosing on fat content, but fruit snacks require consideration of fiber and carbohydrate content as well.
Standard banana consumption guidelines:
- Single medium banana: 50% of typical meal dose
- Large banana or multiple fruits: Full meal dose consideration
- Banana with additions: Adjust based on total macronutrient content
- Smoothie preparations: Calculate total ingredients for appropriate dosing
🔢 Dosing Formula: Most practitioners recommend 500-1000 lipase units per gram of fat consumption, but fruit-based snacks may require 10,000-15,000 total lipase units regardless of fat content due to fiber and carbohydrate complexity.
Adjusting for Fat Content
While bananas contain minimal fat, accompanying foods can significantly alter enzyme requirements. Nut butters, seeds, or dairy additions transform a simple banana snack into a complex meal requiring substantial enzyme support for optimal digestion.
Consider these combination adjustments:
| Banana Combination | Added Fat Content | Suggested Dose Adjustment | Monitoring Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plain banana | 0.4g | Standard snack dose | Sugar absorption, fiber tolerance |
| Banana + almond butter | 8-10g | Increase dose 50-75% | Fat digestion, overall comfort |
| Banana smoothie + yogurt | 3-5g | Increase dose 25-50% | Protein digestion, lactose tolerance |
| Banana bread slice | 5-8g | Full meal dose | Complex carbohydrate breakdown |
Healthcare Provider Consultation
Regular medical oversight ensures optimal enzyme therapy management and prevents complications associated with inadequate or excessive dosing. Healthcare providers can adjust prescriptions based on symptom patterns, nutritional status, and individual digestive responses to different foods.
Schedule provider consultations when experiencing:
- Persistent digestive symptoms despite consistent enzyme use
- Changes in appetite or food preferences affecting nutrition
- Weight fluctuations indicating possible absorption issues
- New medications that might interact with enzyme therapy
- Lifestyle changes affecting meal timing or food choices
📞 Emergency Situations: Contact healthcare providers immediately for severe abdominal pain, persistent diarrhea, or signs of nutritional deficiency that don't improve with enzyme adjustments.
Common Mistakes When Taking Creon with Food
Timing Errors and Digestive Impact
Poor timing represents the most frequent error among Creon users, significantly compromising therapeutic effectiveness and leading to preventable digestive complications. Taking enzymes too late allows food to progress through the digestive tract without adequate enzyme support, resulting in malabsorption, bloating, and nutritional deficiencies.
Critical timing mistakes include:
- Post-meal administration: Enzymes arrive after food has left the stomach
- Inconsistent intervals: Irregular timing disrupts digestive rhythm establishment
- Rushed consumption: Insufficient time for proper enzyme distribution
- Forgotten doses: Complete absence of enzyme support during meals
⏰ Memory Strategy: Use smartphone alarms set 5 minutes before regular meal times to establish consistent pre-dosing habits that become automatic over time.
Temperature Sensitivity Issues
Pancreatic enzymes are highly sensitive to heat exposure, with temperatures above 104°F (40°C) causing rapid protein denaturation and complete loss of enzymatic activity. Many patients unknowingly compromise their medication by combining Creon with hot beverages or foods.
| Temperature Range | Enzyme Stability | Practical Examples | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Below 77°F (25°C) | Optimal stability | Room temperature water, cold foods | Preferred for consumption |
| 77-104°F (25-40°C) | Reduced activity | Warm soup, lukewarm beverages | Use with caution |
| Above 104°F (40°C) | Rapid degradation | Hot coffee, steaming foods | Avoid completely |
| Above 140°F (60°C) | Complete inactivation | Boiling liquids, very hot meals | Never combine |
🌡️ Temperature Test: If you can't comfortably hold the food or beverage for 10 seconds, it's too hot for Creon consumption and will destroy enzyme effectiveness.
Capsule Integrity Mistakes
Maintaining capsule integrity ensures proper enzyme delivery to the intended digestive location. Breaking, crushing, or chewing Creon capsules releases enzymes prematurely, causing mouth irritation and preventing effective food digestion in the small intestine.
Common capsule handling errors:
- Chewing capsules: Releases enzymes in mouth, causing irritation and reducing effectiveness
- Opening unnecessarily: Should only be done for pediatric patients or swallowing difficulties
- Mixing with inappropriate foods: Non-acidic foods can activate enzymes prematurely
- Storing improperly: Heat and moisture can compromise capsule integrity
🔒 Integrity Preservation: Always store Creon in original containers at room temperature, away from moisture and heat sources that can affect both capsule and enzyme stability.
Alternative Snack Options for Creon Users
EPI-Friendly Fruit Alternatives
Diversifying fruit choices prevents nutritional monotony while accommodating varying digestive capabilities and enzyme requirements. Different fruits offer unique nutritional profiles and digestive challenges, allowing EPI patients to customize their diet based on individual tolerance levels and therapeutic goals.
Excellent fruit alternatives include:
- Berries: Low sugar, high antioxidants, moderate fiber
- Melons: High water content, easy digestion, minimal enzyme requirements
- Citrus fruits: Natural acidity supports enzyme function, vitamin C benefits
- Stone fruits: Balanced nutrition, moderate fiber, seasonal variety
- Tropical fruits: Unique enzymes, anti-inflammatory properties, exotic flavors
Dietitian Insight: "Rotating fruit choices ensures comprehensive nutrient intake while preventing digestive adaptation that can reduce enzyme effectiveness over time."
| Fruit Category | Enzyme Requirements | Digestive Benefits | Nutritional Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Berries (blueberries, strawberries) | Low-moderate | Antioxidant support, gentle fiber | Vitamin C, anthocyanins |
| Melons (cantaloupe, watermelon) | Low | High hydration, easy digestion | Beta-carotene, potassium |
| Citrus (oranges, grapefruits) | Low-moderate | Enzyme activation support | Vitamin C, folate |
| Stone fruits (peaches, plums) | Moderate | Balanced nutrition | Vitamin A, fiber |
Balanced Snack Combinations
Strategic snack combinations optimize enzyme utilization while providing sustained energy and comprehensive nutrition. Combining different macronutrients ensures all enzyme types receive activation while preventing blood sugar spikes and energy crashes common in EPI patients.
Effective combination strategies:
- Protein + Carbohydrate: Greek yogurt with berries
- Healthy Fat + Fiber: Apple slices with almond butter
- Complex Carb + Protein: Whole grain crackers with cheese
- Fruit + Nut: Mixed fruit and nut combinations
- Vegetable + Fat: Carrot sticks with hummus
🥜 Combination Benefits: Mixed macronutrient snacks provide longer satiety periods, reducing frequent enzyme dosing requirements while maintaining stable blood glucose levels.
Meal Planning Strategies
Comprehensive meal planning addresses both immediate digestive needs and long-term nutritional requirements for optimal EPI management. Successful strategies incorporate enzyme timing, portion control, and nutritional diversity while accommodating individual lifestyle factors and preferences.
Strategic planning elements include:
- Weekly menu preparation: Reduces daily decision-making stress
- Batch cooking techniques: Ensures consistent food availability
- Emergency snack planning: Prevents missed enzyme doses during busy periods
- Social eating preparation: Strategies for dining out and special occasions
- Seasonal menu adaptation: Takes advantage of fresh, local produce availability
📋 Planning Success: Use meal planning apps or printed templates to track enzyme timing, food combinations, and digestive responses for continuous therapy optimization.
Conclusion
Taking Creon with a banana represents a safe and beneficial combination for individuals managing exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. The fruit's favorable pH level, moderate fiber content, and excellent nutritional profile complement pancreatic enzyme therapy while providing essential vitamins, minerals, and energy. Proper timing, appropriate dosing, and attention to food temperature ensure optimal enzyme effectiveness and nutrient absorption.
The key to successful enzyme therapy lies in understanding how different foods interact with Creon's mechanism of action. Bananas offer an ideal example of strategic food selection that supports digestive health without overwhelming compromised pancreatic function. By following evidence-based guidelines for timing, dosing, and food combinations, EPI patients can maximize their therapeutic outcomes while enjoying diverse, nutritious diets.
Individual responses to enzyme therapy vary significantly, making personalized approaches essential for optimal management. Regular consultation with healthcare providers, careful monitoring of digestive symptoms, and systematic documentation of food responses contribute to successful long-term therapy. With proper attention to these factors, taking Creon with bananas can become part of an effective, sustainable approach to managing pancreatic insufficiency while maintaining quality of life and nutritional health.




